With that in mind, it’s time to learn some terms you’re likely to come across in paid advertising. Keep in mind that these are the terms you’re likely to come across, and not every single term in digital advertising. Without further ado, let’s get started!
- Accelerated Ad Delivery: An ad delivery method that spends your budget faster than a standard ad delivery.
- Ad Delivery: Within AdWords, a setting that determines the pace you want your ads to be shown throughout the day. The two settings are standard and accelerated.
- Ad Extensions: Additional ad features that increase the possibility of a click-through, such as a business’ phone number, address, etc.
- Ad Group: Contains one or more ads which target a shared set of keywords.
- AdMob Ads: Ads that appear within mobile apps through Google AdMob.
- Ad Position: The order in which your ad appears to users in relation to other ads.
- Ad Rank: A value that’s used to determine your ad position, calculated with your bid and quality score.
- Ad Rotation: When you have multiple ads, your ad rotation determines which ad is displayed.
- Ad Scheduling: A setting that allows you to control when and for how long your ads are displayed. This is useful if your target audience is more likely to be online at certain times throughout the day.
- AdWords Ads: These are online ads created within Google’s AdWords
- Audience: Your audience is the group of people you want to view your ad.
- Automatic Bidding: A bidding method whereby your CPC is set automatically for maximum number of clicks. An alternative is manual bidding.
- Automatic Tagging: An alternative to manual tagging, auto tagging automatically appends custom code to the end of a destination URL that is used for tracking purposes.
- Average CPC: The average amount of money that you pay for each click on your ad.
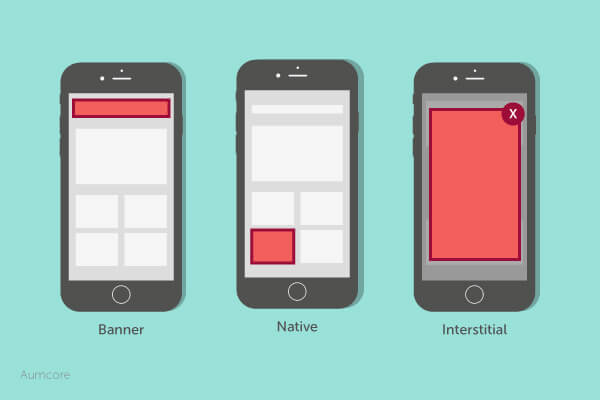
- Banner Ads: Image-based ads that appear in the top, bottom or side of a website, and range in function, design and size.
- Behavioral Targeting: This is when you target an ad at users based on their past purchasing activities. For example, if you sell electronics and someone recently purchased a television, your ad will be shown to them.
- Bid: The amount of money you’re willing to pay for a search keyword click.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of people who land on your site and leave before performing a meaningful action.
- Broad Match: The default match type, broad match displays your ad to a wide audience. Your ad will be displayed if a user’s search includes a word from your keyword (phrase). For example, if your keyword is ‘luxury bags,’ your ad may be displayed to someone searching for ‘luxury watches,’ ‘duffel bags,’ or ‘luxury bag.’
- Call-To-Action (CTA): Phrases or words that drive users to take a specific action such as clicking on your ad.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): A ratio that measures the success of your ad campaign. CTR is measured by dividing the number of ad clicks by the number of impressions.
- Conversion: Conversions range from advertiser to advertiser, but it’s usually used to signify an ad click that lead to a valuable user-action, such as a purchase or registration.
- Conversion Optimizer: A feature that uses historical conversion data to predict which clicks are likely to be valuable.
- Conversion Rate: The average number of conversions per ad clicked. In other words, conversions divided by clicks.
- Cookies: Files saved on a user’s computer that store browsing information.
- Cost-Per-Acquisition (CPA): An advertising option in which you only pay when a lead is generated.
- Cost-Per-Click (CPC): Quite literal, CPC is the amount of money you pay for a single click on one of your ads.
- Cost-Per-Thousand (CPM): One of the two main advertising options you’re likely to encounter (the other is PPC), with CPM you pay a flat rate for every 1,000 impressions. These are usually display ads and relatively cheap because there’s no guarantee that you’ll make a conversion (which means that your money can go down the drain). On the plus side, you have a lot of control and are guaranteed that the ad will be seen.
- Daily Budget: The amount of money you’ve allotted for each ad campaign per day.
- Dayparting: A feature whereby you can specify what time of day your ad will be displayed. You can use it if your target audience is more likely to be online during a particular window of time throughout the day.
- Destination URL: The URL address that users will be taken to once they click on your ad (usually different and longer than the display URL).
- Display Ads: Visual ads, such as a banner ad.
- Display Network: A collection of websites, videos, images, applications, etc. where your ads can appear.
- Display URL: The web address visible on your ad (usually different and shorter from the actual destination URL).
- Enhanced CPC (ECPC): A bid strategy that automatically adjusts your CPC to maximize conversions (it raises or lowers your bid for keywords likely to convert).
- Exact Match: A match type in which your ad is displayed to someone searching for your exact keyword(s). For example, if your keyword is ‘strapless bag,’ your ad may only be displayed to someone searching for ‘strapless bag.’
- Facebook Ads: There are many different types of ads that may be used in Facebook, such as marketplace ads, promoted posts, sponsored stories, and Facebook Exchange (FBX). Use this as your guide to Facebook ads.

- Facebook Exchange (FBX): These are Facebook remarketing ads that use users’ browsing data to determine who to target.
- Flash Ads: Banner ads that use Flash and usually feature interactive elements. These types of ads are not recommended for mobile users because more often than not, they will not be supported.
- Free Clicks: Free clicks are unbilled clicks. These are mainly found in interactive ads that require an initial click, such as a click to start a video.
- Geotargeting: When you geographically target ads to audiences in a specific area (city, state, country, etc.).
- Google AdMob: Google’s mobile advertising platform that creates revenue through free apps with ad space.
- Google AdWords: Google’s online advertising platform.
- Google Analytics: Google’s free web optimization service that provides useful statistics regarding your website’s traffic, users, user behavior, etc.
- Google Display Ads: Banner ads used in the Google Display Network.
- Google Display Network: A collection of websites that host Google Display Ads through Google AdWords.
- Google Merchant Center: A tool provided by Google that allows you to upload product listings for Google Commerce Search, Google Product Ads and Google Shopping.
- Google Search Ads: PPC ads that appear when users queries match your keywords.
- Image Ads: Ads that include graphics (good for engagement).
- Impression: When an ad is displayed to a user, regardless of whether there was a click-through. In other words, when someone views your ad.
- Impression Share: The number of impressions you’ve received divided by the estimated number of impressions you could have received.
- In-App Ads: Ads that appear within an application. You’ll most likely encounter these in games.
- Interest Categories: Interest categories allow you to target people based on their interests (collected from their browsing history across the Google Display Network).
- Key Performance Indicator (KPI): Simply put, a KPI is a metric that measures how you’re performing. This could be conversions, CPA, tc.
- Keyword: A keyword is the word or phrase you can use to target ads. For example, if your keyword is ‘television,’ your ad may appear to someone searching for ‘cheap television,’ ‘new television,’ etc.
- Keyword Tool: There are many keyword tools online, and they serve to help you discover new keywords, estimate traffic volume, check up on competitors, find negative keywords, and more.
- Landing Page: A landing page is the webpage that a user arrives at after clicking on your ad. Make sure to make it relevant to your ad, otherwise you’ll have a high bounce rate.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Keyword phrases with two or more words. These are becoming more prominent with the rise in voice search.
- Manual Bidding: A bidding method whereby you can set your own maximum CPC for your ads. An alternative is automatic bidding.
- Manual Tagging: An alternative to automatic tagging, manual tagging allows advertisers to manually tag destination URLs with “_utm” information that is used for tracking purposes.
- Marketplace Ads: These Facebook ads appear in the side columns with a headline, ad copy and an image.
- Match Type: This controls which searches trigger your ad. The three match types you’ll encounter are broad match, phrase match and exact match.
- Mobile Ads: Ads that appear on mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, etc. Feel free to use this article as your guide to everything related to mobile advertising.
- Negative Keywords: These are keywords you do not want your ads to appear for. In other words, they let you exclude search terms from your campaign. For example, if you’re using broad match and the negative keyword is ‘walking shoes,’ your ad will appear for ‘running shoes’ but not for ‘black walking shoes.’
- Pay-Per-Click: One of the two main advertising options you’re likely to encounter (the other is CPM), with PPC you pay when someone clicks on your ad (price depends on the value of the chosen keyword). These are usually text ads that may have a small image, are easier to track than CPM, and you can place a budget cap to prevent overspending. Unfortunately, there are a lot of accidental clicks, and because you’re competing for ad placements, a click can become very expensive (in the hundreds of dollars per click).
- Phrase Match: A match type in which your ad is displayed to someone searching for something using your keywords, in the exact order. For example, if your keyword is ‘high fashion,’ your ad may be displayed to someone searching for ‘high fashion shoes,’ ‘high fashion bags,’ or ‘buy high fashion.’
- Product Listing Ads (PLA): Search ads that appear under Google Shopping results. These ads feature a product image and are tailored toward particular products or product categories.
- Promoted Posts: Facebook ‘ads’ in which you pay a flat rate to promote a post from a Facebook business page.
- Quality Score: A rating on how well your ad aligns with your marketing message.
- Remarketing: A feature that allows advertisers to show ads to users who have previously visited their website.
- Retargeting Ads: These are ads that use a user’s browsing data to determine who to appear to.
- Return On Ad Spend Spend (ROAS): The ratio of money gained/lost on an investment RELATIVE to the amount of money invested. To calculate ROAS, use the following formula: ROAS = revenue/cost of investment.
- Return On Investment (ROI): The ratio of money gained/lost on an investment. To calculate ROI, use the following formula: ROI = (gain-cost of investment)/cost of investment.
- Search: Just like it sounds, a search is what a user enters in a search engine. When their search matches one of your keywords, your ad may be displayed to them.
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM): Not to be confused with SEO, SEM is a form of online marketing powered by paid advertising for the aim of increasing a website’s visibility.
- Search Engine Results Page (SERP): A literal definition, a SERP is the listings page that appears after a search is made.
- Search Partner: Websites that partner with Google to show your ads.
- Search Term (or Query) Report: A list of search terms that have people have used to not only find your ad, but also click on it.
- Sitelink Extensions: Extensions to AdWords ads that allow you to add more links to your ads, such as to a product page, your company’s information, etc.
- Sponsored Stories: Facebook ‘ads’ that show a user’s interactions with an advertiser’s page or products.
- Standard Ad Delivery: An ad delivery method that spreads your budget throughout the day.
- Text Ads: The standard ad, text ads feature a headline, descriptive text, and a destination URL.
- Tracking Code: A snippet of HTML code that tells you what users do after clicking on your ad.
- Traffic Estimator: An AdWords tool (free!) that predicts how well a particular keyword will perform.
- Twitter Ads: Ads in which you pay to get a boost to increase the reach of your tweets.
- View-Through Conversion: A type of conversion tracking within Google that provides a measurement of how many users say your Google Display Network ad but did not click on it.
And we are finished! If you want to know more about a specific term here (or one that wasn’t mentioned), feel free to drop a comment!






Tell us your thoughts in the comments